Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers in 2026: A Simple Guide to Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a basic idea in engineering. It explains how heat moves from one place to another. We see heat transfer every day. A hot cup warms our hands. A refrigerator removes heat to keep food cold.
In industries, heat transfer is very important. Machines, plants, and buildings all need good heat control. One of the most common tools used for this purpose is the shell and tube heat exchanger.
In 2026, shell and tube heat exchangers are still widely used. They are strong, reliable, and easy to maintain. This guide explains shell and tube heat exchangers and heat transfer in a very simple way.
What Is Heat Transfer?
Heat transfer means the movement of heat from a hot object to a cooler one. Heat always flows from hot to cold.
There are three main ways heat moves:
-
Conduction – heat moves through a solid
-
Convection – heat moves through a fluid (liquid or gas)
-
Radiation – heat moves as energy waves
Shell and tube heat exchangers mainly use conduction and convection.
What Is a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger?
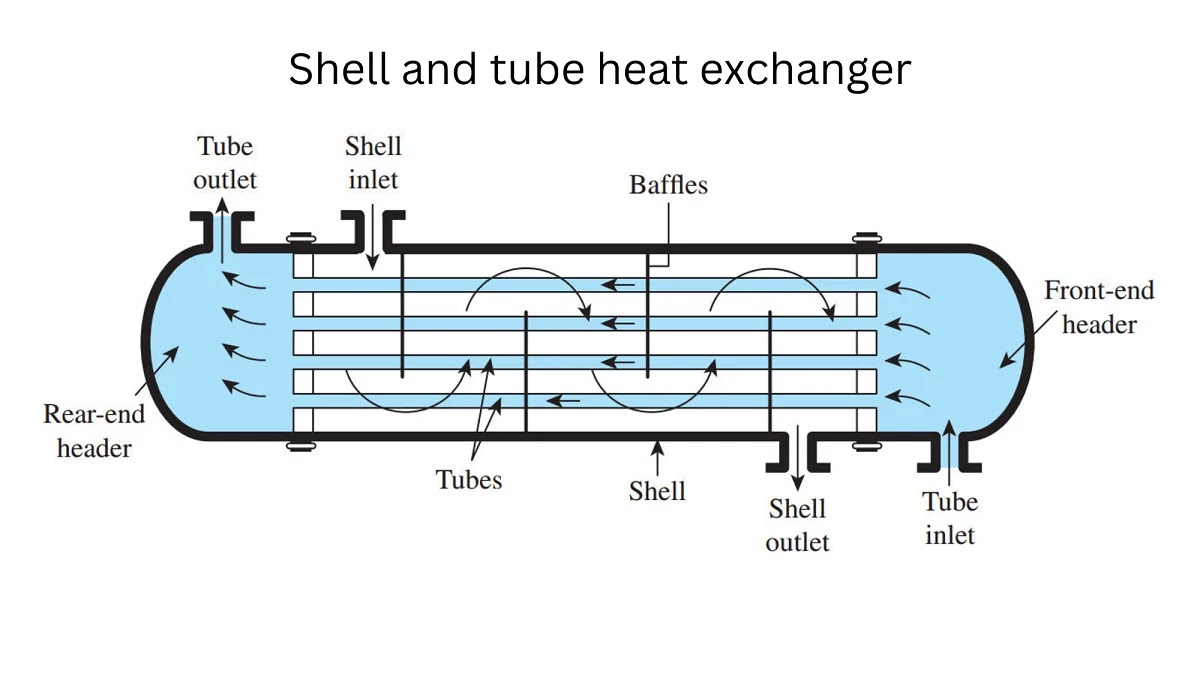
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between two fluids.
It has two main parts:
-
Tubes
-
Shell
One fluid flows inside the tubes.
Another fluid flows around the tubes inside the shell.
The two fluids do not mix. Heat moves from the hot fluid to the cold fluid through the tube walls.
Why Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Are Important
These heat exchangers are popular because they:
-
Handle high pressure
-
Work at high temperatures
-
Are easy to clean
-
Last a long time
In 2026, industries still trust them for safe and steady operation.
Basic Parts of a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Let us look at the main parts in simple words.
Tubes
Tubes carry one fluid. Heat passes through the tube walls.
Shell
The shell is the outer body. It holds the second fluid.
Tube Sheets
Tube sheets hold the tubes in place.
Baffles
Baffles guide the fluid and improve heat transfer.
Inlet and Outlet Nozzles
These allow fluids to enter and leave the exchanger.
How Heat Transfer Happens in Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Heat transfer happens in steps:
-
Hot fluid enters the tubes
-
Cold fluid enters the shell
-
Heat moves through the tube walls
-
Cold fluid becomes warmer
-
Hot fluid becomes cooler
This process happens continuously.
Role of Conduction
Conduction happens inside the tube walls.
Heat moves from the hot fluid to the tube material.
Then heat moves through the tube wall to the other side.
Good tube materials help heat move faster.
Role of Convection
Convection happens in the fluids.
When fluids move, heat spreads more evenly.
Faster flow usually means better heat transfer.
Both tube-side flow and shell-side flow use convection.
Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
There are different designs based on flow patterns.
Parallel Flow
Both fluids flow in the same direction.
Counter Flow
Fluids flow in opposite directions.
This design gives better heat transfer.
Cross Flow
Fluids move at right angles.
In 2026, counter-flow designs are commonly used for better efficiency.
Tube Side vs Shell Side
Tube Side
-
Fluid inside the tubes
-
Easier to clean
-
Handles high pressure
Shell Side
-
Fluid around the tubes
-
Better mixing with baffles
-
Used for large flow rates
Engineers choose based on fluid type and pressure.
Design Factors That Affect Heat Transfer
Several design choices affect performance.
Tube Material
Common materials include:
-
Stainless steel
-
Copper alloys
-
Carbon steel
Better materials transfer heat faster.
Tube Diameter and Length
Smaller tubes increase surface area.
Longer tubes allow more heat transfer time.
Tube Arrangement
Tubes can be arranged in:
-
Triangular pattern
-
Square pattern
Arrangement affects flow and cleaning.
Baffle Design
Baffles:
-
Increase turbulence
-
Improve heat transfer
-
Reduce fouling
In 2026, improved baffle designs reduce energy loss.
How Engineers Improve Heat Transfer Efficiency
Engineers use several methods to improve performance.
Increasing Surface Area
More surface area means more heat transfer.
This is done using:
-
Finned tubes
-
Extended surfaces
Increasing Turbulence
Turbulence helps fluids mix better.
Methods include:
-
Baffles
-
Twisted tubes
-
Turbulators
Controlling Flow Rate
Proper flow speed improves heat exchange.
Too slow or too fast reduces efficiency.
Fouling and Its Effects
Fouling means dirt or scale builds up on surfaces.
It causes:
-
Reduced heat transfer
-
Higher energy use
-
Maintenance problems
In 2026, anti-fouling coatings and monitoring systems help reduce fouling.
Maintenance of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Regular maintenance is important.
Common steps include:
-
Tube cleaning
-
Leak inspection
-
Pressure testing
-
Temperature monitoring
Good maintenance extends service life.
Applications Across Industries
Shell and tube heat exchangers are used in many fields.
Power Plants
They cool steam and condensers.
Petrochemical Industry
They heat and cool process fluids.
HVAC Systems
They support heating and cooling in buildings.
Food and Beverage Industry
They pasteurize and cool products safely.
Pharmaceutical Industry
They control temperatures during production.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers in 2026
In 2026, technology improves performance and safety.
Modern features include:
-
Smart sensors
-
Digital temperature control
-
Predictive maintenance
-
Energy optimization software
These upgrades reduce downtime and energy waste.
Advantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Key benefits include:
-
High durability
-
Wide temperature range
-
Easy repair
-
Long life
-
Flexible design
This makes them suitable for many applications.
Limitations to Consider
They also have some limits:
-
Large size
-
Higher initial cost
-
Heavy weight
Engineers must choose carefully based on needs.
Shell and Tube vs Plate Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube exchangers:
-
Handle high pressure
-
Are stronger
-
Need more space
Plate heat exchangers:
-
Are compact
-
Transfer heat faster
-
Work best at lower pressure
Both types are useful.
Why Heat Transfer Knowledge Matters
Understanding heat transfer helps:
-
Save energy
-
Improve safety
-
Increase efficiency
-
Reduce costs
Engineers rely on these principles daily.
Simple Summary
Shell and tube heat exchangers:
-
Transfer heat between fluids
-
Use conduction and convection
-
Are widely used in industry
-
Remain important in 2026
They support modern engineering systems around the world.
Final Thoughts
Shell and tube heat exchangers show how simple heat transfer ideas solve real problems. They move heat safely and efficiently in many industries.
In 2026, better materials and smart tools improve their performance. Even with new technologies, shell and tube heat exchangers remain a trusted solution.
Understanding them helps engineers design better systems and save energy for the future.